Safe mode (sometimes called safe boot) is a way to start up your Mac so that it performs certain checks and prevents some software from automatically loading or opening. Starting your Mac in safe boot mode does the following:
- Verifies your startup disk and attempts to repair directory issues, if needed
- Loads only required kernel extensions
- Prevents startup items and login items from opening automatically
- Disables user-installed fonts
- Deletes font caches, kernel cache, and other system cache files
- Rolls back partially installed updates
It is an excellent fix for “stuck” startup bars. Often this issue is caused by incompatible startup items, bad HDD sectors or faulty updates. Safe boot will allow you to isolate startup issues, fix sectors and re-install dropped updates.
Start up in safe boot mode
Safe boot mode is accessed when you switch on the computer:
- Start or restart your Mac, then immediately press and hold the Shift key. The Apple logo appears on your display. Along with a startup bar that may move much more slowly than anticipated – Not only is this bar showing you the progress of the startup but it is also showing you the progress of any automated repairs/rollbacks it may be preforming.
- Release the Shift key when you see the login window. If the startup disk is encrypted with Filevault you might be asked to log in twice: once to unlock the startup disk, and again to log in to the Finder.
To leave safe mode, restart your Mac without pressing any keys during startup.
If you don't have a keyboard or if you can't use the Shift key
If your Mac doesn’t have a keyboard available to start in safe mode, but you have remote access to your Mac, you can configure the Mac to start up in safe boot mode using the command line.
- Access the command line by opening Terminal remotely, or logging into the computer using SSH.
- Use the following Terminal command:
sudo nvram boot-args="-x"If you want to start in verbose mode as well, use this instead:sudo nvram boot-args="-x -v" - After using safe mode, use this Terminal command to return to a normal startup:
sudo nvram boot-args=""
How to tell if your Mac has started in safe mode
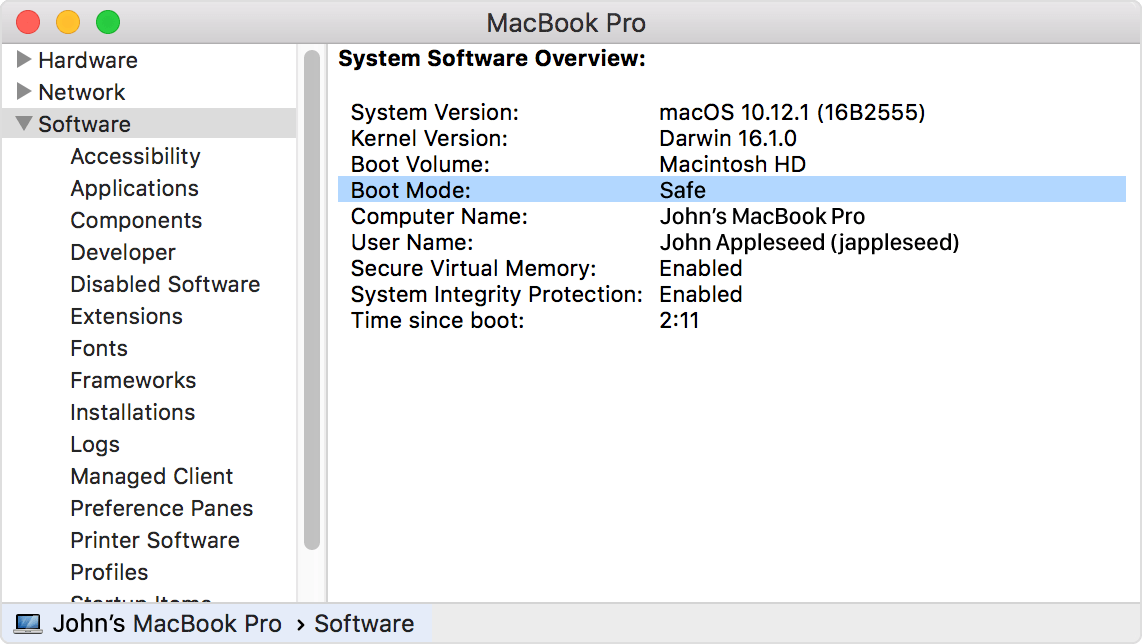
If you’re not sure that your Mac is started in safe mode, you can use System Information to check. The Software section of System Information lists Boot Mode as “Safe” instead of “Normal” in these cases.
The login window will also display “Safe Boot” in the upper-right corner of the screen when your Mac is in safe mode.